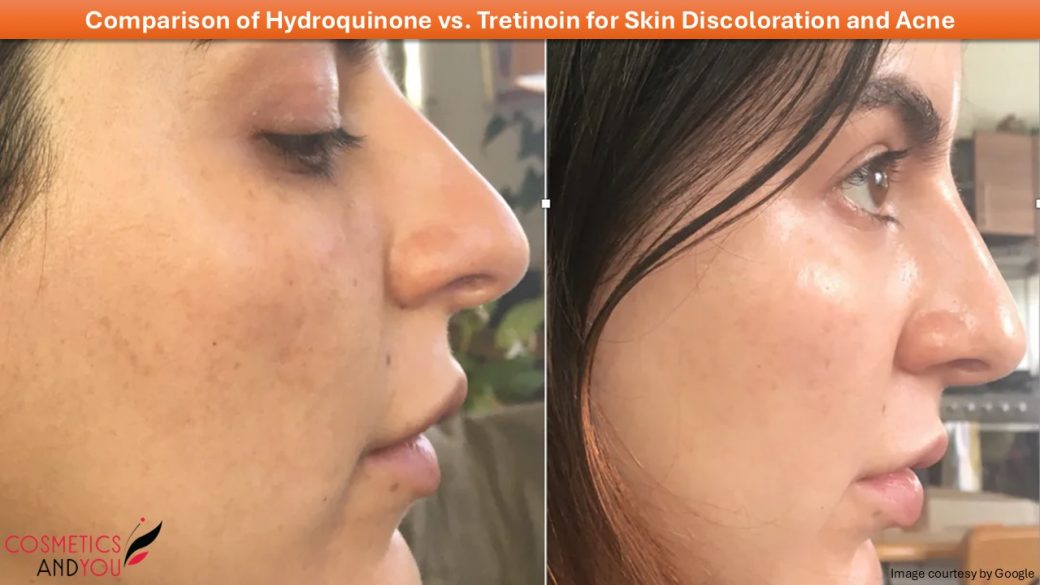
Acne and skin discolouration greatly impact inconvenience and self-confidence, especially when it appears in moderate to severe conditions. Although both are very common skin concerns, they require attention to be cured. Timely care and treatment help reduce the severity of these skin issues. Markets are flooded with thousands of products that claim to be effective against various skin issues, but very few deliver the results. One should be careful when selecting products to treat acne or skin discolouration problems.
This page will help you identify one of the best ingredients that can offer relief from stubborn skin issues.
Hydroquinone and Tretinoin are popular and effective topical dermatological treatments to address various skin concerns, including hyperpigmentation and acne. While both are effective in their own ways, they have distinct mechanisms of action and are often combined to achieve better results. Let’s compare their effectiveness, uses, benefits, and potential side effects.
Action mechanism
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a skin-lightening agent that works by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is crucial in melanin production. This leads to a reduction in pigmentation and the disappearance of dark spots over time. Individuals dealing with melasma, age spots, or significant hyperpigmentation are prescribed hydroquinone.
Tretinoin
Tretinoin is a retinoid derived from Vitamin A. It works by increasing cell turnover, encouraging the shedding of old skin cells, and promoting new cell growth. It reduces acne and fine lines and improves skin texture. Tretinoin can also help lighten hyperpigmentation indirectly by accelerating the skin’s renewal process.
Uses of Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone treats melasma, sunspots/age spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation caused by acne, burns, or other skin traumas. Hydroquinone 4 cream is often combined with other active ingredients (like tretinoin or corticosteroids) for enhanced effects.
Benefits:
- Effective at reducing dark spots and evening out skin tone.
- Often shows visible results within 4-6 weeks, although full effects may take several months.
Uses of Tretinoin
Tretinoin treats acne, fine lines, and wrinkles, improves rough skin texture, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. It improves the appearance of uneven skin tone and texture, including post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Benefits:
- Clinically proven to treat acne and prevent future breakouts.
- Helps reduce fine lines, smooths skin, and improves skin elasticity.
- Effective at reducing post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially when combined with other agents like hydroquinone.
Combination therapy
Hydroquinone and tretinoin are often used together, especially in prescription products, to maximise results while minimising irritation. This combination is particularly effective for stubborn cases of melasma and severe hyperpigmentation. Hydroquinone reduces pigment production by decreasing melanin production. Hydroquinone gradually lightens areas of hyperpigmentation over several weeks to months.
Tretinoin enhances the penetration of hydroquinone, improving its efficacy. The combination can simultaneously address hyperpigmentation and acne, with tretinoin improving skin texture and hydroquinone targeting discolouration. Tretinoin enhances cell turnover, allowing hydroquinone to penetrate more deeply and work more effectively. Adding a corticosteroid (in combination formulations) helps reduce irritation from tretinoin.
Popular prescription combination
Tri-Luma is a popular prescription combination formulation containing Hydroquinone 4%, Tretinoin 0.05%, and Fluocinolone Acetonide 0.01%.
Usage direction
Hydroquinone is typically recommended for short-term use, typically up to 4-6 months. It’s often cycled with other lightening agents (like azelaic acid or kojic acid) to maintain results.
Tretinoin can be used long-term, but it may take 8 to 12 weeks to see noticeable improvements, especially for acne. Continuous use provides the best anti-ageing benefits.
Precautions
Both hydroquinone and tretinoin can cause photosensitivity, so it’s crucial to use sunscreen daily to prevent further skin damage and to optimise treatment outcomes.
Introducing tretinoin gradually is essential to avoid skin irritation; start with lower concentrations or use it every other night.
Side effects of hydroquinone
- Skin irritation, redness, and dryness.
- Ochronosis (rare but possible): A bluish-grey skin discolouration due to prolonged use.
- It should not be used long-term; it is typically recommended for up to 3 months, with breaks in between.
Side effects of tretinoin
- Initial temporary worsening of acne.
- Skin dryness, redness, peeling, and increased sensitivity to the sun.
- It may take several weeks to months to see full benefits. Top of Form Bottom of Form
Best formulation to use:
- Hydroquinone is usually recommended if your primary concern is dark spots or melasma.
- If you’re looking to treat acne, prevent signs of ageing, or improve overall skin texture, tretinoin is a more suitable option.
- For stubborn hyperpigmentation and melasma, a combination of both agents might be prescribed.
Always use sunscreen daily when using hydroquinone or tretinoin, as both can increase skin sensitivity to UV rays. To experience the best results, consult a dermatologist before starting treatment, especially if considering a combination therapy.
Conclusion
Hydroquinone and tretinoin are powerful tools in treating skin concerns, but choosing the right one depends on your specific skin goals. Hydroquinone is best for targeted discolouration, while tretinoin is excellent for a broader range of skin concerns, including acne and anti-ageing. When used together under dermatological guidance, they can offer powerful results for hyperpigmentation and skin texture issues.