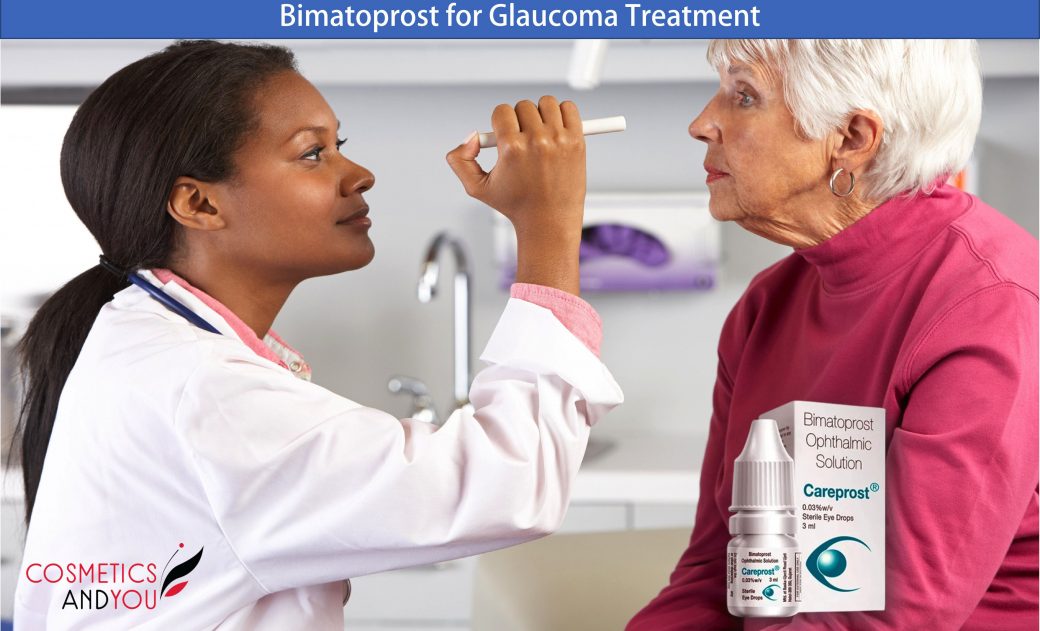
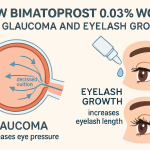
Bimatoprost is a prostamide that has been proven highly effective as monotherapy, adjunctive, and replacement therapy for lowering intraocular pressure and providing good control of intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
Bimatoprost for the treatment of glaucoma
Ophthalmic topical bimatoprost is a prostaglandin that has received approval from the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of lowering intraocular pressure (IOP). Evidence suggests that topical bimatoprost is among the most effective medicines for reducing IOP in eyes, ocular hypertension, and primary open-angle glaucoma. Glaucoma is an eye disorder characterised by the chronic progression of visual field defects due to the loss of retinal ganglion cells. Glaucoma treatment aims to control the progression of visual field defects. Research studies indicate that control of visual field defects is associated with a decrease in IOP. Typically, a decrease in the IOP is achieved by administering single-drug eye drops.
Growth of eyelashes is a well-documented side effect of bimatoprost during the treatment of glaucoma. Later, the FDA approved ophthalmic bimatoprost to treat hypotrichosis of eyelashes, such as for patients post-chemotherapy. Due to its longer, darker, and thicker eyelashes, bimatoprost 0.03% ophthalmic solution is often purchased for cosmetic purposes. The ophthalmic product is available at 0.03% in the United States when used to lower IOP; daily dosing of bimatoprost may be used alone or with another drug.
Mechanism of action in the reduction of intraocular pressure
It has been well documented that bimatoprost and several topical prostaglandin analogues sustainably and effectively reduce IOP and are used as a standard first-line treatment of open-angle glaucoma. This is achieved primarily through enhancing aqueous through the uveoscleral pathway. It is shown that lowering IOP in glaucoma and ocular hypertension patients may reduce the risk of disease progression.
Applying bimatoprost ophthalmic solution for open-angle glaucoma
Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.03% may be applied directly to the ocular surface as an eye drop. The usual dose of bimatoprost is one drop every evening, although it may vary depending on the ophthalmologist’s dosing. A patient should wait at least five minutes between administering bimatoprost and other ophthalmic medications. With bimatoprost, a 0.03% reduction in IOP should begin after four hours, and the effect will peak at twelve hours, maintaining the reduced IOP through 24 hours. Research reports over the past year demonstrate that bimatoprost effectively lowers IOP in the long term and is generally well tolerated.
Side effects
Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated the high levels of safety and tolerance of bimatoprost when applied to the ocular surface. Several studies on bimatoprost eye drop application have revealed that, aside from transient eyelash prominence, the most common side effects include eye pruritus, conjunctival hyperaemia, burning irritation, dry eye syndrome, eye pain, visual disturbances, foreign body sensations, and pigmentation of the eyelid margin. Use of this ophthalmic agent may not be appropriate for some people with closed-angle glaucoma and inflammatory or neovascular glaucoma. Contact lenses should be removed before applying this ophthalmic solution. Lenses can be reinserted after fifteen minutes.
Contraindications
Bimatoprost is contraindicated in people with a medical history of bimatoprost hypersensitivity or hypersensitivity to other Intraocular applicators containing bimatoprost. Bimatoprost eye drops for glaucoma are contraindicated in infants and children due to concerns about pigmentation changes associated with long-term use. The safety and effectiveness of bimatoprost application for hypotrichosis have not been studied in children and infants under five years of age. The usage should not be considered if the potential benefits justify the risks. This careprost ophthalmic agent has not been adequately studied in pregnant women.
Summary: Patients on bimatoprost therapy achieve and maintain low IOP levels throughout the day and night, and long-term trials have demonstrated that the effectiveness of bimatoprost is sustained. The ophthalmic agent has been proven to be safe and well-tolerated in clinical trials, and, as a once-daily medication, allows for patient convenience, resulting in improved treatment compliance. It is the most effective ophthalmic solution for protecting the visual field in patients with ocular hypertension and glaucoma.