Retinoids have long been celebrated as a gold standard in skincare. From tackling acne to reducing fine lines and evening out skin tone, they are among the most researched and dermatologist-recommended ingredients. Among the many retinoid-based products available, A Ret Gel stands out for its effectiveness, accessibility, and versatility. But what makes A Ret Gel different from other retinoid creams on the market? Let’s delve into its formulation, benefits, and how it compares to similar products.
What Is A Ret Gel?
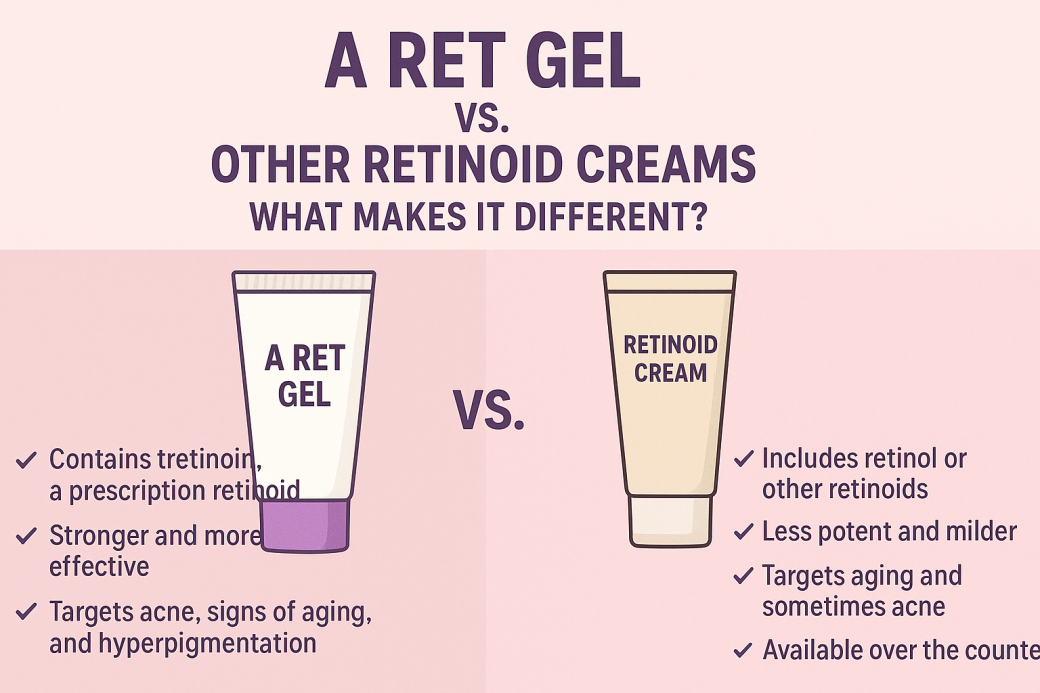
A Ret Gel is a topical retinoid formulation that contains tretinoin, a derivative of Vitamin A. Tretinoin is a prescription-strength retinoid often used to:
- Treat acne (especially comedonal acne, blackheads, and whiteheads)
- Reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles
- Improve skin texture and tone
- Address hyperpigmentation and sun damage
Unlike over-the-counter retinol creams, A Ret Gel is considered more potent and delivers faster, clinically proven results when used correctly.
The Science Behind Retinoids
Retinoids are compounds derived from Vitamin A. They work at the cellular level by:
- Increasing cell turnover – helping shed dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- Stimulating collagen production – improving firmness and reducing wrinkles.
- Regulating pigmentation – fading dark spots and evening out skin tone.
- Controlling sebum production – making them especially useful in acne management.
However, not all retinoids are created equal. There are different types with varying strengths and purposes.
A Ret Gel vs. Over-the-Counter Retinol Creams
Strength and Potency
- A Ret Gel (Tretinoin): Prescription-strength, significantly more potent. Results are usually noticeable within 6–12 weeks.
- Retinol Creams: Weaker, require conversion in the skin to become active. Results may take several months to appear.
Target Concerns
- A Ret Gel: Best for moderate to severe acne, sun damage, fine lines, and stubborn hyperpigmentation.
- Retinol Creams: Ideal for beginners or individuals with sensitive skin seeking gentle anti-ageing and acne prevention.
Who Should Use It?
- A Ret Gel: Suitable for individuals with persistent acne or advanced signs of ageing, under medical supervision.
- Retinol Creams: Ideal for first-time retinoid users or those seeking maintenance skincare.
A Ret Gel vs Adapalene (Differin and Similar Gels)
Formulation
- A Ret Gel (Tretinoin): A first-generation retinoid with proven effectiveness for acne and anti-ageing.
- Adapalene: A third-generation retinoid, slightly gentler and more stable in sunlight.
Efficacy
- A Ret Gel: Works more aggressively; excellent for stubborn acne and visible anti-ageing results.
- Adapalene: Highly effective for acne but less proven in anti-ageing benefits compared to tretinoin.
Irritation Levels
- A Ret Gel: Can be irritating during the adjustment phase (peeling, dryness, redness).
- Adapalene: Generally better tolerated by sensitive skin.
A Ret Gel vs. Retinoid Creams for Anti-Ageing
When it comes to anti-ageing, dermatologists often prefer tretinoin-based products like A Ret Gel over OTC retinol. Why?
- Collagen Boosting Power: A Ret Gel stimulates collagen more efficiently.
- Faster Results: Noticeable improvement in wrinkles, fine lines, and skin texture within a few months.
- Clinical Backing: Tretinoin has decades of research proving its anti-ageing efficacy, making it the benchmark in dermatology.
Other retinoid creams may promise similar results but often fall short in terms of potency and speed.
Benefits of Choosing A Ret Gel
- Proven Track Record: Tretinoin has been in clinical use for over 40 years.
- Multi-Purpose: Treats acne, pigmentation, and ageing simultaneously.
- Prescription-Strength Results: Outperforms most cosmetic creams in effectiveness.
- Availability in Gel Form: Lightweight and less greasy compared to heavy creams, making it ideal for oily or acne-prone skin.
- Long-Term Skin Health: Encourages healthier, more resilient skin with continued use.
Possible Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Like other strong retinoids, A Ret Gel can cause initial irritation, often referred to as the “retinization phase.” Symptoms may include:
- Redness
- Dryness
- Peeling
- Mild burning sensation
Tips to Reduce Side Effects:
- Start with a pea-sized amount 2–3 times a week.
- Always apply at night (retinoids are photosensitive).
- Pair with a gentle cleanser and moisturiser.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen daily.
- Gradually increase frequency as your skin adjusts.
Who Should Avoid A Ret Gel?
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Individuals with extremely sensitive skin or eczema
- Those with a history of severe skin allergies should not consult a dermatologist.
Key Differences Summarised
| Feature | A Ret gel | Retinol Creams | Adapalene Gels |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | Prescription, very potent | Over-the-counter, mild | Prescription/OTC, moderate |
| Results | 6–12 weeks | 3–6 months | 8–12 weeks |
| Best For | Acne, anti-aging, pigmentation | Beginners, mild concerns | Acne (sensitive skin) |
| Irritation | Higher initially | Lower | Lower than tretinoin |
Final Thoughts
When comparing A Ret Gel to other retinoid creams, its main advantage lies in strength and proven clinical efficacy. While retinol and adapalene have their roles, especially for beginners or sensitive skin, A Ret Gel remains the gold standard for those seeking visible, long-term improvements in acne, pigmentation, and signs of ageing.
If you’re considering A Ret Gel, it’s wise to consult a dermatologist to ensure it suits your skin type and concerns. With proper use, patience, and consistency, A Ret Gel can truly transform your skin and give you the clear, radiant complexion you’ve been working toward.